A
ACTH
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone. This hormone is produced by the pituitary gland and flows through the blood to the adrenal glands to tell them to produce more cortisol.
Adenoma
A benign tumor or growth. A pituitary adenoma is not cancerous.
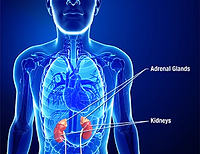
Adrenalectomy
Surgical removal of the adrenal glands.
ADH
Anti-diuretic hormone or vasopressin. This hormone is produced by the pituitary and causes the kidneys to conserve body fluids.
Agonist
An agonist is a molecule that triggers the same effects and actions as a naturally occurring molecule or hormone. It stimulates or activates cellular responses just like the natural hormone. For example, a dopamine agonist causes the same effect on cells as dopamine itself by binding to the same receptor on the surface of cells. This causes the cell to respond in the same way as it would in the presence of the real hormone.
Antidiuretic Hormone (Vasopressin)
The pituitary hormone that controls water balance.
B
Bromocriptine
A drug of a type called dopamine agonists can be used to reduce prolactin production in people with prolactinomas. Its brand name is Parlodel, and it was produced by Novartis.
C
Cabergoline
A drug of a type called dopamine agonists can be used to reduce prolactin production for people with prolactinomas. Its brand name is Dostinex, and it is produced by Pfizer.
Cortisol
One of the hormones produced by the adrenal glands. It is particularly important in times of stress and illness.
Craniopharyngioma, Rathke’s Cleft Cyst
A problem that occurs during fetal development (in the womb) that may grow at any time in life, not a cancer or brain tumor, often causes loss of pituitary function and may cause diabetes insipidus.
Corticotropin-releasing hormone is normally made by the hypothalamus to stimulate ACTH production. In synthetic form, it is used to test for pituitary-dependent Cushing's disease.
Cushing's Disease
Cushing's syndrome is caused by a tumor of the pituitary gland.
Cushing's Syndrome
Caused by overproduction of cortisol for any reason.
D
DHEA
5-Dehydroepiandrosterone is a steroid naturally produced by adrenal glands and synthesized in the brain. It is a prohormone considered to be a precursor for sex steroids.
Diabetes Insipidus
A form of diabetes that results from water imbalance and is characterized by frequent urination and excessive thirst.
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter is made in the brain that regulates prolactin secretion. The medicines used to treat prolactinomas are effective because they are designed to increase the action of dopamine.
Dopamine Agonists
Dopamine agonists such as bromocriptine (brand name Parlodel) and cabergoline (brand name Dostinex) inhibit GH release from the tumor. They work by stimulating natural receptors of the hormone dopamine on the surface of the tumor. This sends messages to the tumor cells to stop producing GH.
E
Ectopic ACTH
Production of ACTH from a site other than the pituitary gland.
Endocrine
Relating to hormones.
Endocrine System
The body-wide system of hormone-producing glands and the hormones they make control many aspects of life, including growth and reproduction.
Endocrinologist
A doctor who specializes in treating hormone illnesses.
F
Florinef
A medication that controls salt and water balance.
Frequency of Acromegaly
In every million people, three cases of acromegaly are diagnosed each year.
FSH
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone. This is one of the two pituitary hormones (with LH) that is released from the testes in men and the ovaries in women.
G
Galactorrhea
A medication that controls salt and water balance.
Gigantism
Gigantism is a serious disorder where a person has grown very large and tall due to excess secretion of growth hormone from the pituitary gland during childhood. The height of people suffering from this disorder can reach eight feet. For more information on this condition, please visit http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=4914.
Growth Hormone (GH)
As the name suggests, growth hormone (GH) stimulates physical growth in children. It is a hormone that is produced by the pituitary gland and has widespread effects on the body. After you have stopped growing at 17 or 18, the skeleton changes and is no longer able to increase in height. However, growth hormones still play important roles in adulthood, such as maintaining muscle tone and regulating metabolism, energy levels, and psychological well-being.
H
Hormone
A chemical substance produced by the endocrine glands of the body works by sending messages through the bloodstream.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is the term used for any pharmaceutical/drug therapy given to an individual to provide particular hormones that are missing or present at an abnormally low level. If the pituitary gland is not functioning, specific hormonal therapy will be prescribed to replace those hormones that the gland would normally produce.
Hydrocortisone
The drug name of cortisol is when it is made into a tablet or injection.
Hyperprolactinemia
A medical condition in which a patient has elevated blood levels of prolactin, most often due to a pituitary tumor (a prolactinoma). Normal prolactin levels are less than 25 ng/ml in women and less than 17 ng/ml in men. In addition to a pituitary tumor, some medications, hypothyroidism, and kidney disease can lead to elevated serum levels of prolactin.
Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is a disorder in which the pituitary gland does not produce the normal amounts of some or all of its hormones. Hypopituitarism can affect several systems and cause growth failure in children, low thyroid hormone production (necessary for metabolism), low cortisol (steroid) production, and loss of reproductive function (loss of menstrual cycles in women, low testosterone in men and problems with fertility in both men and women). This is an uncommon condition, and all missing hormones can be replaced.
I
IGF-1
IGF-1 is a very important hormone involved in growth and development, and it is made by many tissues in the body. IGF stands for insulin-like growth factor, but you will probably hear the hormone referred to as “I-G-F-one.”
Insulin
Insulin is a hormone secreted by a group of islet cells within the pancreas, which is an organ located near the stomach. Most cells in the body have insulin receptors that bind to circulating insulin, which triggers the cell to absorb glucose (sugar). Without insulin, cells are starved because they cannot access the calories contained in the glucose.
L
LH
Luteinizing Hormone. This hormone is produced by the pituitary and sends messages to the reproductive organs (called gonads) – the ovaries in women and testes in men. In children, LH contributes to sexual development. In women, it works together with FSH to control ovulation and is thus essential for a normal menstrual cycle and for fertility. In men, FSH stimulates the testes to produce sperm.
M
Macroadenoma
A prolactinoma that is 10 mm or larger.
Microadenoma
A prolactinoma that is smaller than 10 mm (or about 1/2 inch).
MRI Scan
Magnetic resonance imaging is a type of scan that produces a clear image and is used to determine the size and location of the tumor.
O
Oxytocin
The pituitary hormone that causes contraction of the uterus during labor.
P
Pegvisomant
Pegvisomant is a growth hormone antagonist. It does not lower the level of GH released from the tumor, but it stops the hormone from acting on its targets in various parts of the body. This then prevents the effects of too much GH, such as overproduction of IGF-I. To do this, pegvisomant binds to the natural receptors for growth hormone and gets in the way of the hormone being able to bind and send messages into cells. Imagine forcing the wrong key into a lock; the correct key cannot then fit in, and the lock cannot be opened.
Pergolide
A drug that is used to reduce prolactin production in people with prolactinomas. Its brand name is Permax, and it is produced by Eli Lilly.
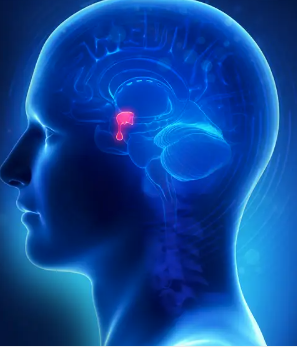
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is an important gland, and it is often referred to as the 'master gland' because it controls several of the other hormone-producing glands. It is usually about the size of a pea and is situated in a bony hollow beneath the base of the brain and just behind the bridge of your nose. The gland consists of two parts (often called lobes), each of which has different functions. The pituitary gland is also sometimes called the hypophysis.
PRL
Prolactin. This hormone is produced by the pituitary gland and is usually best known as the ‘milk hormone’ because its main purpose is to stimulate the breasts to produce milk after childbirth. However, men and women produce prolactin all the time. Its purpose in men is unclear.
Prolactin
A hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates the production of breast milk during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
Prolactinoma
An abnormal growth, or tumor, on the pituitary gland. The tumor is almost always noncancerous (benign) and causes the pituitary to produce too much prolactin, which leads to hyperprolactinemia.
Q
R
Radiosurgery
Finely targeted radiation therapy using MRI to pinpoint the tumor.
Radiotherapy
Radiation treatment, usually used after surgery, prevents the regrowth of the tumor. Radiotherapy has a long-acting effect and may cause a reduction of some of the other pituitary hormones over time, thus requiring them to be replaced.
Receptors
A receptor is a specialized protein on the surface or interior of a cell that interacts only with very specific molecules in the surrounding environment. Receptors enable molecules or drugs outside cells to communicate a signal to the interior, causing a response within that cell.
S
Somatostatin Analogues
These mimic a natural hormone called somatostatin and latch onto the hormone’s natural receptors on the surface of the tumor. When this ‘lock and key’ connection is made, specific signals are sent into the tumor cells to make them stop producing GH.
Stimulation Test
Stimulation testing is conducted when your healthcare provider suspects you are not producing the appropriate amount of a hormone. The test varies depending on which hormone is being evaluated, but the test typically involves a pretest phase during which you may be required to fast or eat a very specific diet, and then a blood sample is collected.
T
Thyroid
The thyroid is a gland that lies over the windpipe and just below the larynx. It produces hormones that are essential to numerous body processes.
TSH
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone. A hormone produced by the pituitary sends a message to the thyroid gland to increase or decrease its production of the hormone thyroxine.
Transsphenoidal Surgery
A method of operating on the pituitary gland by making an incision in front of the upper teeth and behind the upper lip, or alternatively inside the nose. This allows the surgeon access to the pituitary via the sphenoid sinus and minimizes trauma to the patient.